- AI Meets Healthcare
- Posts
- 🤝 Robot performs surgery with skill of human doctor #1
🤝 Robot performs surgery with skill of human doctor #1
AI Meets Healthcare Newsletter: Bridging AI and Medicine — Daily News & Insights
Welcome to the first issue of AI Meets Healthcare — bridging medicine and AI from a doctor's perspective. I'm Alisa, a medical doctor from Denmark.
I'll be curating the most interesting AI healthcare news every weekday. I'm not an AI expert, but I'm very curious about how AI is impacting healthcare. This first issue covers highlights from the past few weeks, with daily updates (Monday-Friday) starting tomorrow.
Highlights from past few weeks
Microsoft’s new AI model: BiomedParse, all-in-one biomedical image analysis
AI Chatbots Defeated Doctors at Diagnosing Illness
10 new LLMs (Large Language Models) in Life science released in last few weeks
AI-powered robot performs surgery with skill of human doctor
Microsoft’s new AI model: BiomedParse all-in-one biomedical image
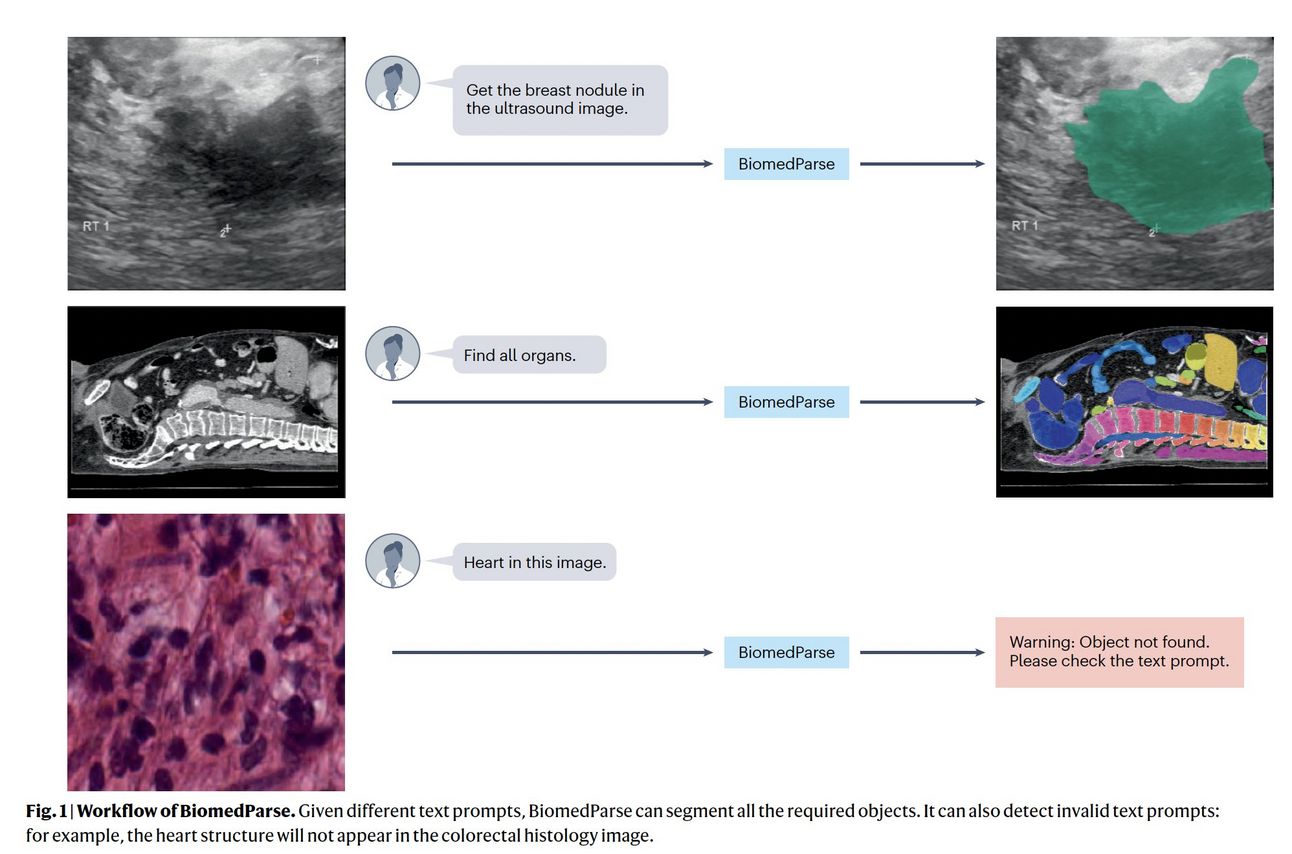
BiomedParse is a new AI model that makes analyzing medical images more efficient by combining 3 tasks that were previously done separately:
Recognition: identifying what's in an image.
Detection: finding where objects are located.
Segmentation: outlining specific areas in pixels.
The model can handle 9 different types of medical images and understands written descriptions of what to look for.
It was trained on over 6 million images paired with text descriptions, and performs better than existing tools, especially when dealing with irregularly shaped objects in medical images.
Instead of using multiple different tools, doctors and researchers can now use BiomedParse as a single solution for analyzing various types of medical images.
🎥 Microsoft introducing BiomedParse
AI Chatbots Defeated Doctors at Diagnosing Illness
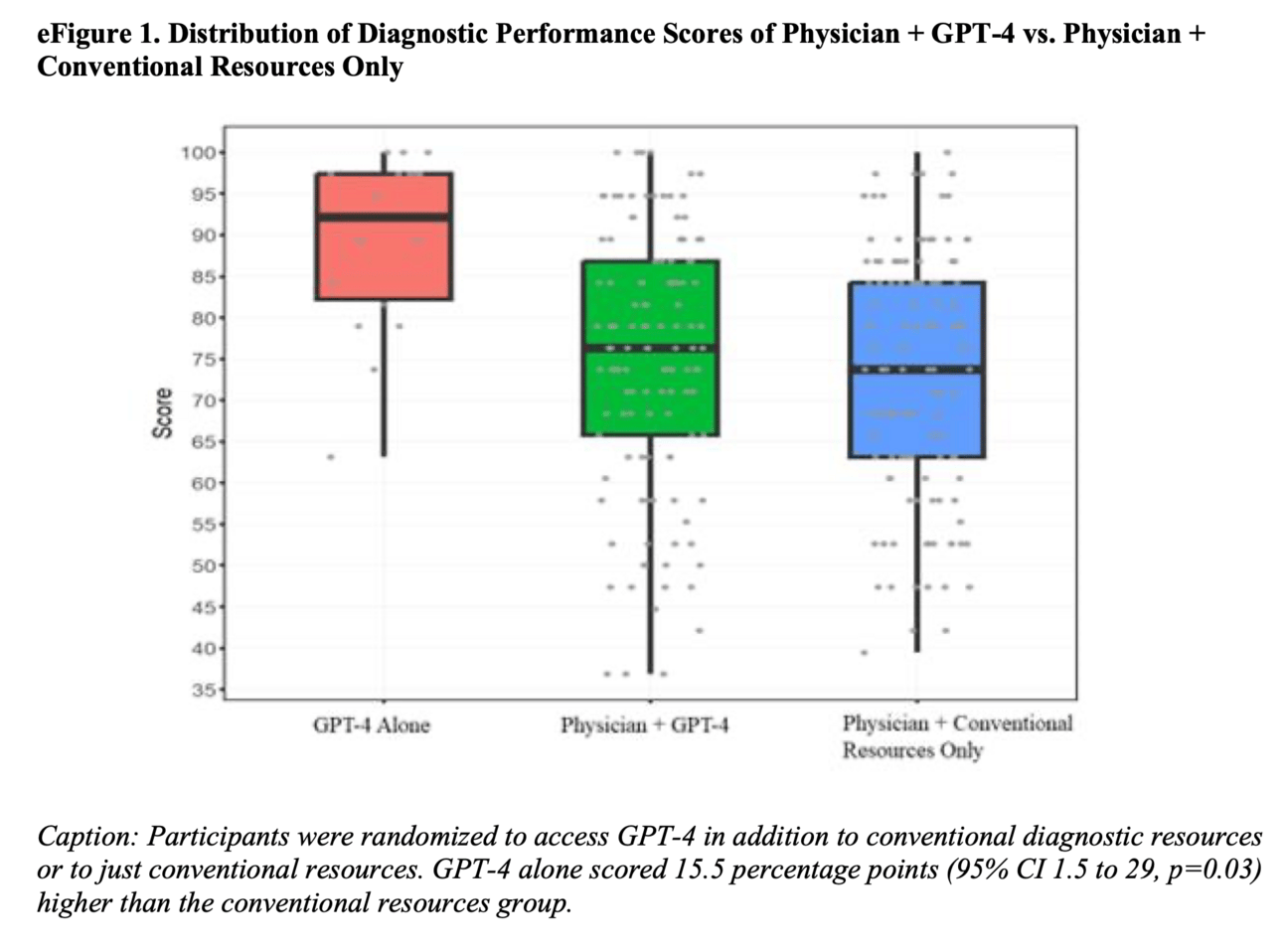
A new study showed that AI alone performed better than both ‘physician + AI’ and ‘physician + conventional resources only’.
Study limitations:
The sample size was small with only 50 participants and 6 medical cases. While these cases were carefully chosen, this limited number can't represent the full variety of medical cases.
Participants weren't trained in prompt engineering (techniques to get more accurate AI responses)
Participants could choose how and when to use the AI system - this was done on purpose to match how they would use it in real hospital settings.
10 new LLMs (Large Language Models) in Life science released in last few weeks

Cover by N. Burgess (Science) and Claire Agouti (Nature), taken from ‘Ground Truth’ newsletter
Before ChatGPT captured global attention, AlphaFold2's breakthrough in protein folding not only won the 2024 Nobel Prize and transformed scientific research across 190 countries, but also sparked an explosive wave of AI models in life sciences - with 10 new large language models (LLMs) published just the past few weeks, a speed of progress that nobody imagined possible.
💡What is a large language model (LLM)?
It's a type of artificial intelligence that can understand and generate text by identifying patterns in massive amounts of data.
The new LLMs in Life science: Evo, Human Cell Atlas, BOLTZ-1, RhoFold, EVOLVEPro, PocketGen, MassiveFold, RhoDesign, MethylGPT, CpGPT and PIONEER (published last month)
I recommend reading this excellent post written by Dr. Eric Topol, a physician-scientist, which gives a clear overview.
🎥 AI for Science conference, in London this week, hosted by Google DeepMind & the Royal Society of Medicine.
AI-powered robot performs surgery with skill of human doctor
Johns Hopkins University researchers, along with Stanford University researchers, have developed a surgical robot that learns by observing expert surgeons. This breakthrough helps accelerate the path to surgical autonomy, reducing medical errors and improving surgical accuracy.
Key features:
Imitation Learning: The robot learned surgical techniques by analyzing hundreds of videos from the da Vinci Surgical System, which is widely used worldwide, bypassing the need for manual programming.
Adaptive Accuracy: the team trained the robot to perform 3 tasks: manipulate a needle, lift body tissue, and suture — as skillfully as human doctors.
Error Recovery: If the robot drops a needle, it automatically picks it up and continues the procedure, showcasing its adaptability.
Thanks for reading! Found this helpful? Subscribe to get daily AI healthcare insights in your inbox and never miss an update. Feel free to share with colleagues who might be interested.
Until next time,
Alisa